What are Precision Tweezers?
Tweezers are simple yet diverse tools that are well suited for several types of applications. They are made up of two connected “arms” that stand in tension and form an elongated V-shape. When squeezed together tweezers create a grip, which can be used by those working on highly detailed tasks where high levels of precision are required.
What are the different Types of Tweezers?
Tweezers come in assorted sizes, strengths, and tip sizes. Each type serves a specific purpose, there will be several factors you should be considering before choosing a pair of tweezers -
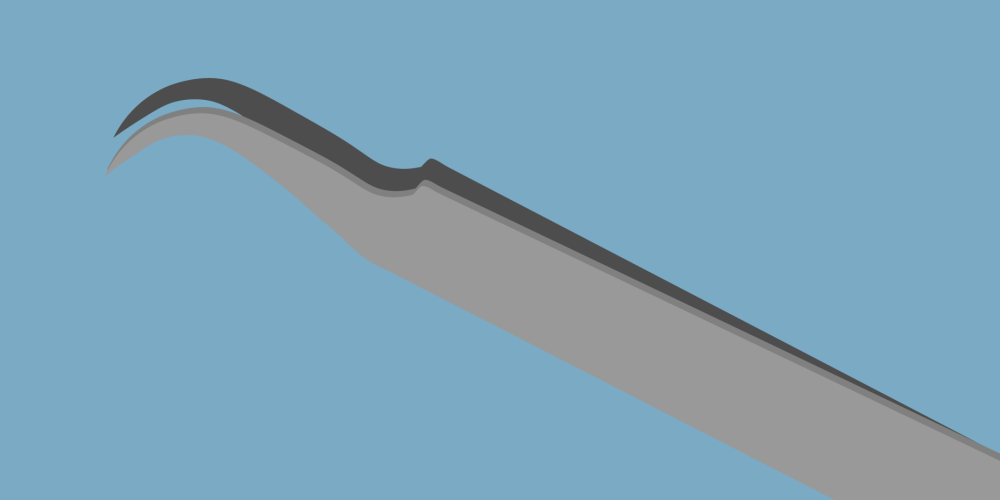
Bent/Curved - allows the user to have easy control and accuracy at a comfortable angle, which can help in reducing operator fatigue.
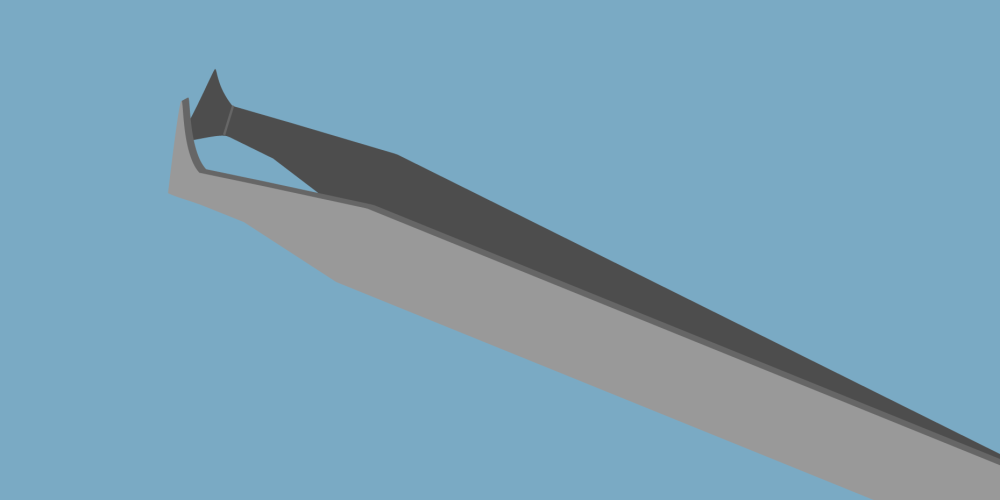
Blunt – the finely curved tips makes these tweezers best suited in applications that could result in a component getting damaged or entangled if a sharp pointed pair of tweezers were used.
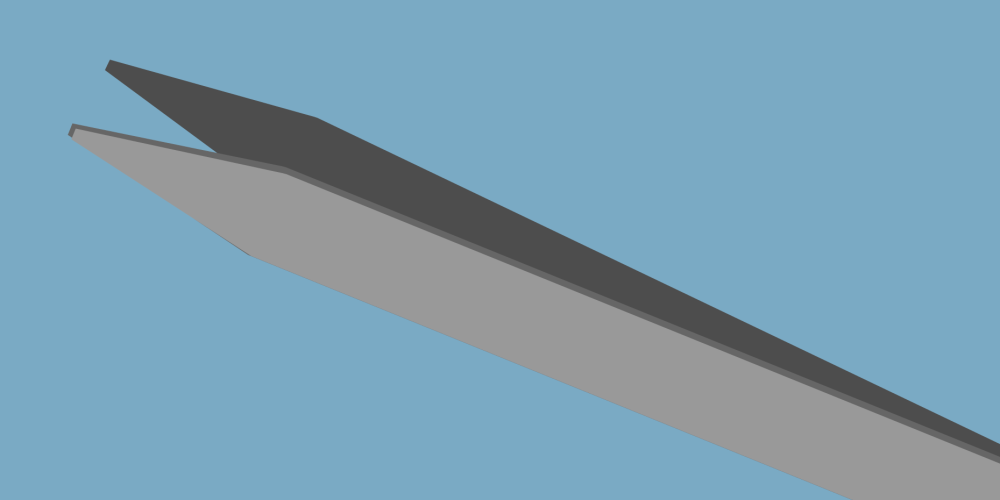
Cutting - sharp edges allow the user to cut through things such as soft wires.
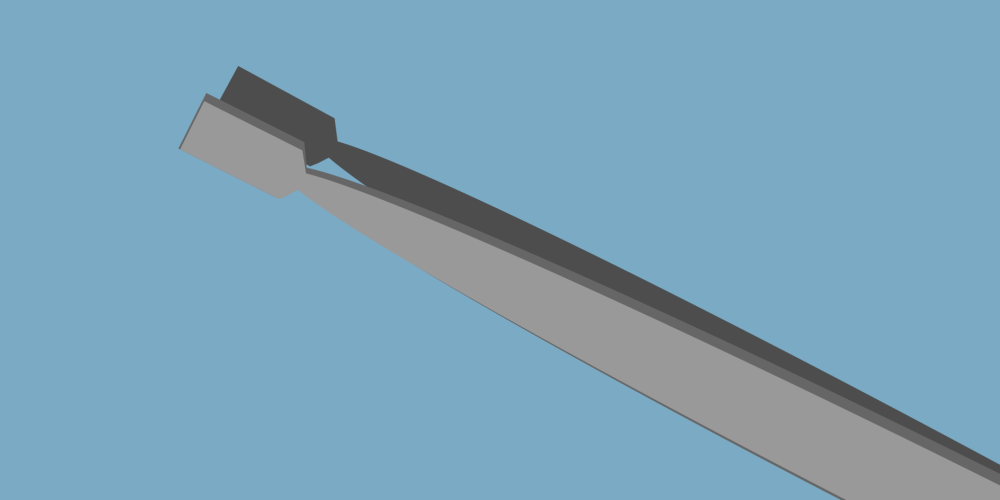
Flat - used for picking up larger objects, as they offer a larger surface area than standard tweezers.
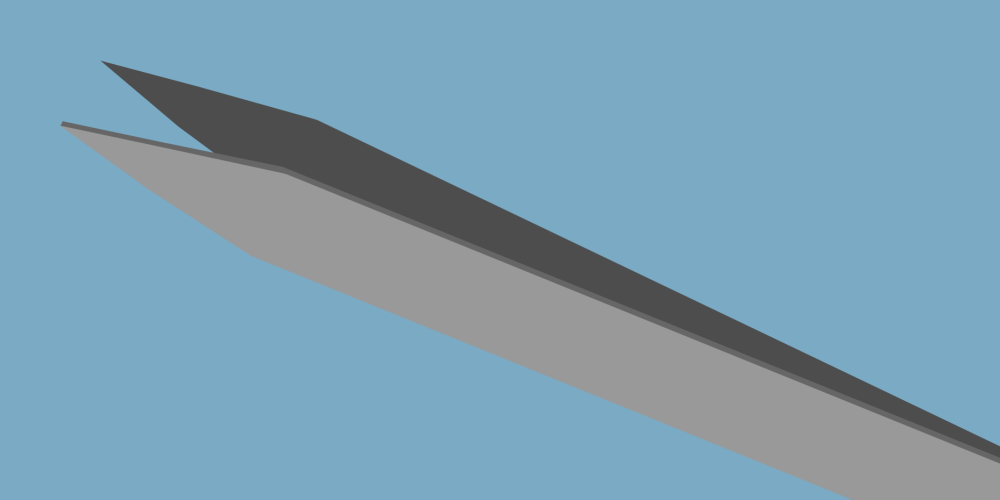
Pointed - used for reaching into small and hard to reach areas.
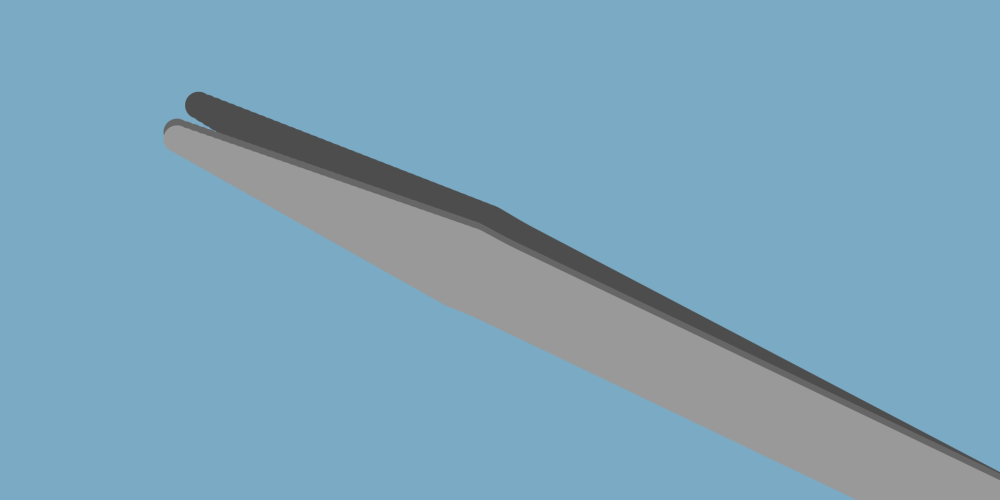
Round - general-purpose tweezers that are used where high levels of precision aren’t required.
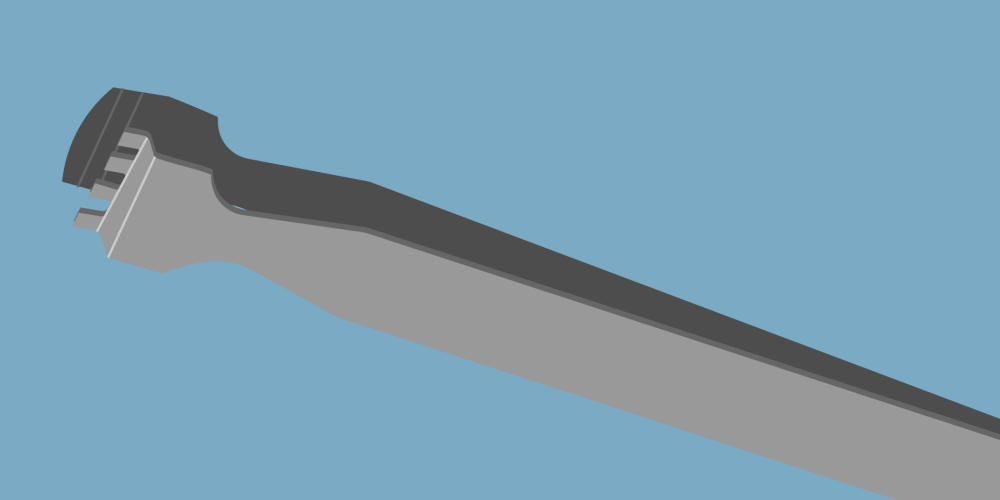
Wafer – the flat tips on these tweezers enable the safe handling of silicon wafers in the manufacturing of semiconductors, without damaging them.
Features of Tweezers
- Tweezers allow the user to hold, handle and grab small components or objects.
- Some include a serrated tip to create a secure grip.
- Some tweezers will have a ridged sides that enhance grip and control when handling an object.
- ESD coatings offer additional safety and versatility when working with electrically sensitive equipment and components (read more about ESD tweezers below).
- Other common features include anti-corrosion, anti-magnetism and solder adhesion resistance for greater functionally across different applications.
Working with Electronics
When working with electronics you should not be using standard tweezers in which you would remove splinters or hairs with, because there is a chance that they are made up from a generic metal.
Working with electronics generally means you will be working with components and circuit boards, so ESD tweezers are ideal because they prevent static electricity passing through to the circuit board and rendering it worthless.
What is ESD?
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) is the abrupt flow of electricity between two differently charged objects when they encounter one another. In extreme circumstances, ESD can cause explosions and destroy equipment.
ESD safe tweezers should always be used when working with static sensitive devices like resistors, capacitors, and semiconductors.
“ESD safe” tweezers are made of a static dissipative material or are coated to limit the peak current at which static discharge occurs, preventing sparks. ESD tweezers are critical for manufacturing microelectronics, watches and medical device components. They come in a variety of materials and shapes, for your specific needs, whether you manufacture PCBs, assemble aerospace electronics, repair phones or anything that uses electricity!
ESD Tweezer Materials
Carbon steel tweezers are extremely durable, highly magnetic, and great for high precision tasks, however, this type of steel will rust and stain throughout its life.
Non-magnetic, high precision, non-scratching plastic tweezers are made of carbon fibre, are lead-free and resistant to 102 Ohm/sq. These tweezers conduct well, yet also have low surface resistivity and can be used at temperatures up to 130°C – 190°C.
Epoxy coated antimagnetic electronics tweezers are coated with an ESD safe epoxy with a resistance of 105 – 106 Ohm/sq. and can be used up to 120°C. The tough polymer coating provides a good grip and enhances resistance to acids, alkalis, and oxidation. Prolonged contact with organic solvents should be avoided though.
Industries that use these tweezers include biological sciences, electronics manufacturing, microscopy preparation and watchmaking.
Anti-magnetic stainless-steel tweezers contain low carbon and alloys such as chromium, nickel and molybdenum, which makes them non-magnetisable, as well as chemical and corrosion-resistant.
Plastic tweezers are made of stable composites that never present the risk of conducting electricity and can be used to add or remove objects from corrosive solutions. They can also be sterilised in hot water and are easily disposable, which makes them popular when working with toxic materials.
NOTE: stainless steel tweezers are useful for many clean rooms and general lab applications however they are not ESD safe.